Ballard Cut Prentiss Architects
2013-05-07 01:00
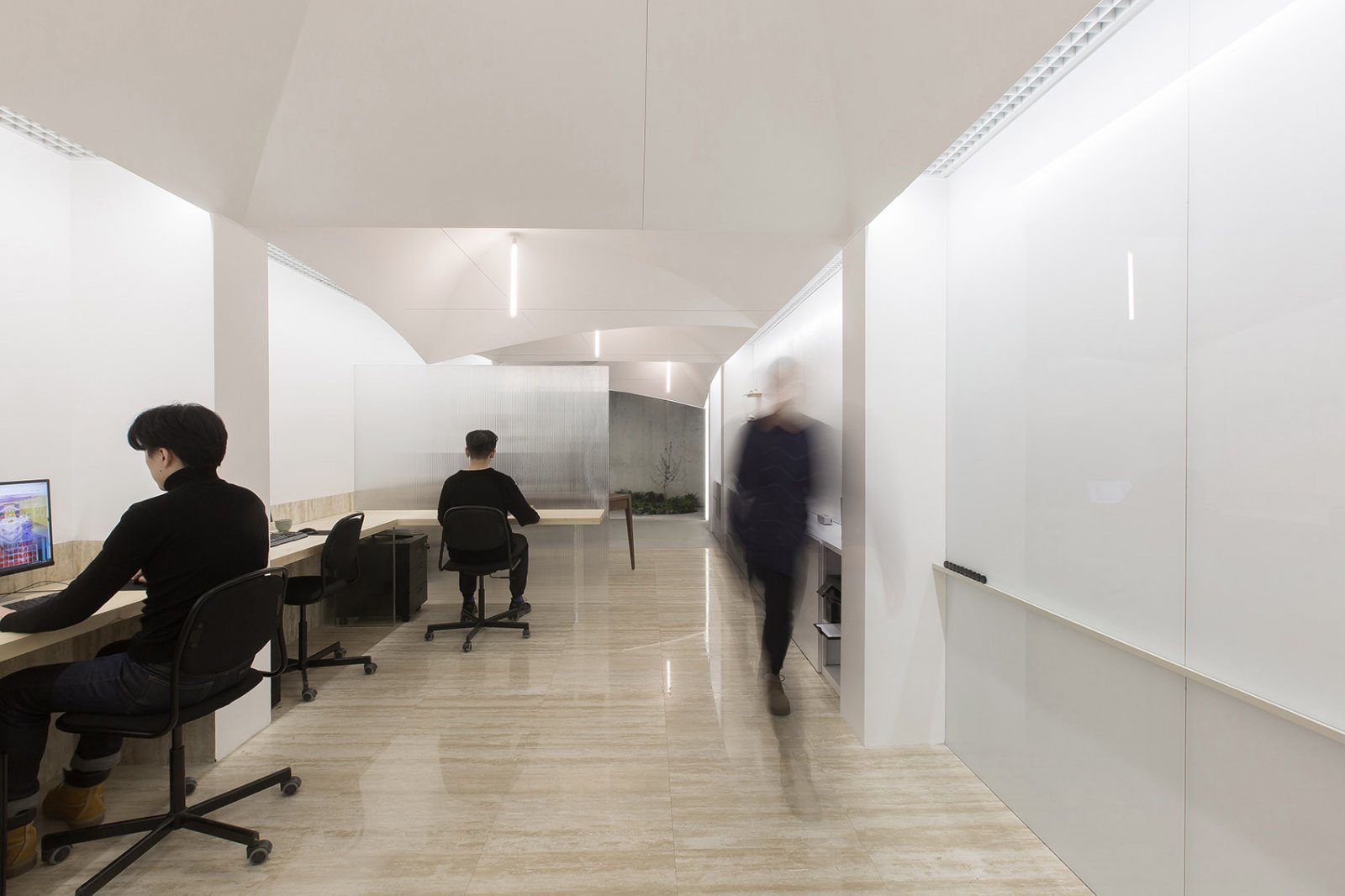
架构师提供的文本描述。该项目位于一个困难的高度管制的地点,向西有一个陡峭的斜坡,东部有一个大的铁路地役权和倒退。为了应对这些挑战,将混凝土地基和地窖设置为离斜坡所需的距离,并将房屋的框架部分延伸到陡峭的斜坡缓冲层上,以达到水景的目的。这种将卷和元素扩展到其他部分的方法在整个项目中进行,最终建立一个简单的部分,由两个堆叠的矩形卷组成,并将其提升到站点之上。第二层的音量从第一层空间的轴线旋转,形成一个有盖的入口、一个楼梯围护、通往屋顶花园的通道,并将卧室、浴室和办公室聚焦到声音和奥林匹克山脉的景色上。
Text description provided by the architects. The project is sited on a difficult highly regulated site with a steep slope to the west and a large railroad easement and setback to the east. In response to these challenges the concrete foundation and cellar are set the required distance back from the slope and the framed portion of the house is extended over the steep slope buffer to access the water view. This method of extending volumes and elements over others is carried throughout the project ultimately establishing a simple parti of two stacked rectangular volumes that elevate over the site. The second floor volume is rotated from the axis of the linear first floor volume, creating a covered entry, a stair enclosure, access to a roof garden, and focusing the bedroom, bath and office to views of the Sound and the Olympic Mountains.
集中和开窗是通过大量的火车活动的东方。线性方案允许东墙作为一道屏障,使房屋内部和西院免受铁路噪音的影响。虽然西面的海拔高度很大程度上是为了进入水景和山景,但东墙很少有开口来保持声音保护所需的坚实性。
Massing and fenestration are informed by the heavy volume of train activity to the east. The linear scheme allows for the east wall to act as a barrier to insulate both the interior of the house and the west yard from the railroad noise. While the west elevation is largely glazed to allow access to the water view and the view of the mountains, the east wall has few openings to maintain the solidity necessary for sound protection.
通往这所房子的通道是沿着一条木板路走的,那条步道高高地耸立在一个沉陷这个花园空间和可接近的绿色屋顶对希望在船上居住14年后过渡到陆地的客户来说很重要。
Access to the house is along a board walk that is elevated over a sunken garden. This garden space and the accessible green roof were important to the clients desiring a transition to terra firma after residing on a boat for 14 years.
最低限度的廉价完成材料托盘被用来实现规模经济和减少过渡细节。例如,一种廉价的混凝土纤维板被用于大多数外部表面,通过更小面积的雪松壁板而更加突出。选择紧结粗糙的雪松,而不是昂贵的清澈的雪松。这种粗糙度与光滑的混凝土纤维板是平衡的,以达到既和谐又经济的目的。在西面的海拔高度需要大量的玻璃。与其安装昂贵的幕墙系统,更便宜的铝制钉鳍窗户被组合在一起,并与铝断口形状修整,以达到类似的效果,降低成本。
A minimal pallet of inexpensive finish materials was used to achieve an economy of scale and reduce transition details. For example; an inexpensive concrete fiber board was used for most exterior surfaces, accented by smaller area of cedar siding. Tight-knot rough cedar is selected rather than expensive clear cedar. This roughness is balanced with the smooth concrete fiber board to achieve both harmony and economy. Extensive glazing was desired on the west elevation. Rather than install an expensive curtain-wall system, less expensive aluminum nail-fin windows were ganged together and trimmed with aluminum break shapes to achieve a similar effect for a reduced cost.
 举报
举报
别默默的看了,快登录帮我评论一下吧!:)
注册
登录
更多评论
相关文章
-

描边风设计中,最容易犯的8种问题分析
2018年走过了四分之一,LOGO设计趋势也清晰了LOGO设计
-

描边风设计中,最容易犯的8种问题分析
2018年走过了四分之一,LOGO设计趋势也清晰了LOGO设计
-

描边风设计中,最容易犯的8种问题分析
2018年走过了四分之一,LOGO设计趋势也清晰了LOGO设计









































 PintereAI
PintereAI